Introduction |
This manual has been designed to assist in the proper preparation of the D1 Professionalizing document, the first step in constructing the Final Project (FP).
Here you will find the necessary information to complete the mandatory fields for this document, as well as some examples to better understand it.
Initial considerations |
The following are some important details to keep in mind when developing the document:
- Prolonged use of capital letters should not be used, that is, sentence format should always be used, exactly as has how this is written.
- Writing in sustained capitals is considered a sign of discourtesy and is difficult to readf or many, as well as in computer language it is interpreted as a virtual shout.
Item 1: Study program name |
This data is fundamental for analyzing the relevance of the final project theme proposal with the study program in which you are enrolled. It is important to detail the specialty/elective if the studied program includes it. Consult the PANAL for the study program’s proper name as indicated in the figure below:  Some double degree programs may have different names for each university. If applicable, select only one and complete the field with the name of the study program.
Some double degree programs may have different names for each university. If applicable, select only one and complete the field with the name of the study program.
Item 2: Student name |
Write your full first and last names without abbreviations.
Item 3: Type of professionalizing project |
a) Project design: this is a project that already has a specific design approved and endorsed by an academic community. It is a type of project that is frequently repeated and well-known in the area of knowledge to which the study program developed by the student is attached. It originates from an identified problem or opportunity. Example: a business plan in the area of business and entrepreneurship.
b) Intervention project: this is a type of project that, not having a specific procedure validated by the academic community, adopts a general methodology: diagnosis and solution proposal. It involves a project in which specific knowledge of the study program developed by the student is applied, but the way it is developed applies to all areas of knowledge.
Item 4: Title of the proposed FP |
- Length: The title should be short. There is no exact number, and the student will need to evaluate the situation. If it is possible to express the title with 10 words instead of the initially planned 13 words, then it is evident that there are 3 surplus words, which can be eliminated.
- Reliability: The title must be true to the content of the work and represent the essence of the project. The paper’s title can refer to the theme or its general objective.
- Comprehensibility: The title must be absolutely understandable, that is to say, that the person who reads the title clearly understands what it discusses. It is a common misconception that only experts in the field will read the paper. The title must be clear and understandable to any level of reader.
Item 5: Project justification |
a) Project scope. The people, materials, organizations, or as appropriate, affected by the lack of the project are quantitatively supported.
b) Project significance. Indicates the medium- and long-term repercussions brought about if the project is not carried out.
c) Project feasibility. The possibility of carrying out the project is stated, taking into account the availability of human, material, technological, temporal, bibliographic and financial resources.
d) Project vulnerability. The scope of a given circumstance determined on the basis of the information obtained.
Item 6: Objective description |
When writing objectives, it is best to use verbs from the cognitive dimension of the taxonomy, as these are aimed towards understanding and knowledge of a topic. The following table suggests verbs from the cognitive dimension of the taxonomy according to levels of learning:
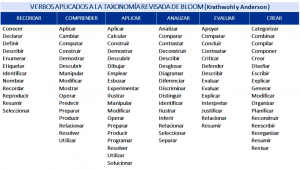
Item 7: Initial situation: problem to be solved or opportunity to be seized |
a) Inform the population and/or manage the necessary permissions for the intervention, if necessary.
b) Conduct a documentary review on the subject in question for an improved initial approach.
c) Identify potential problems and difficulties when carrying out the diagnosis, as well as alternatives for action and solution.
Item 8: Methodology for the collection and treatment of information |
Initially, describe the actors and/or participants who will provide information for the construction of the proposal, and how they were chosen. Specifically, a certain number of people should be mentioned and their participation justified; depending on the approach, inclusion and exclusion criteria may be used; and finally, if a probabilistic calculation is chosen, the sample equation for finite or infinite populations should be used as appropriate. Also, the instruments to be used for data collection should be defined at this stage. Some of these could be: interview guide, questionnaire format, Likert scale, checklist, observation guide, etc. All Professionalizing Approach projects include the collection of empirical data, meaning all must involve fieldwork. For example, for the marketing plan, market research will be conducted, and questionnaires will be applied to 360 people, this number was obtained using the equation for finite populations, applying the same inclusion and exclusion criteria described in psychographic segmentation. The questionnaire was validated by González Ortega (2004) and consists of 30 closed questions and 10 open ones.
Item 9: FP Proposal structure |
If it was decided to opt for an Intervention Project, the proposal should have, roughly speaking, the following elements:
|
INTERVENTION PROPOSAL (This example is useful for all intervention projects) |
|---|
|
|
If it was decided to opt for a Project Design, the proposal must adhere to what is established by the area of knowledge in which the proposal falls under. For example, a business plan, which is attached to the area of Business Administration, may have the following elements:
|
PROJECT DESIGN (This example is only useful for the area of business administration) |
|---|
|
|
|
|
But this is only an example for the case of Project Design and each area of knowledge has projects that use particular structures, for example, a civil work plan, a nutritional plan, an educational proposal, a human development plan in the area of psychology, etc.
Item 10: FP Indicators |
- If the proposal is about a Problem, then these indicators should be to reduce or minimize the negative impacts of the problem in question.”
- If the proposal is based on an Opportunity, then these indicators should be to increase and improve the impacts.
Some criteria for defining indicators for the project are:
- Verify the degree of achievement of the general objective and ‘intermediate objectives’ (milestones), by evaluating the degree of achievement of the planned goals.
- Measure the activities carried out, specify their percentage of adjustment to what was planned, and estimate their contribution to achieving the objectives. If possible, identify opportunities for improvement.
- Determine what resources have been effectively used and with what ‘intensity’, assessing efficiency. The real versus the estimated.
- Evaluate project management processes and identify improvements based on lessons learned.
- Understand the valuation of stakeholders, using instruments that reflect, for example, satisfaction with the products and deliverables, in the case of business projects.
In the organizational context, KPIs can be used. The term KPI (Key Performance Indicator) refers to a set of metrics used to synthesize information about the effectiveness and productivity of actions carried out in a project, in order to make decisions and determine which have been most effective in meeting the objectives set in a specific process or project. KPIs are also known as quality indicators or key project indicators and can be used and applied in any professionalizing approach project.
Item 11: Bibliography |
At this stage, the bibliography should only be those references that will provide theoretical support to the project. References must be academic/scientific, such as books, theses and scientific articles. As a general rule, no web pages should be presented, with rare exceptions. References should be current, except for those bibliographies considered fundamental historical frameworks for the project. How many bibliographies should be submitted in FP-D1? 5 – 10 main bibliographic references should be presented so far. What citation standard should be used to present bibliographies? In general, students will follow the APA Guidelines (here), except for students whose Final Projects are related to Health Sciences, who will follow the Vancouver Guidelines (here). Below is an audiovisual content related to the Vancouver Citation Standard and the APA Citation Standard:
- EBSCO: https://www.ebsco.com/e/es-es
- LILACS: http://lilacs.bvsalud.org/es/
- Directory of Open Access Journals: https://doaj.org/
- SciELO: www.scielo.org/php/index.php
- AMLC Journal Network: www.redalyc.org
- ScienceDirect: http://www.sciencedirect.com/
- Elsevier: http://www.elsevier.com/advanced-search
- Dialnet: http://dialnet.unirioja.es/
- Google Scholar: http://scholar.google.es/
- PubMed: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed